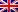
احصائيات البحوث المنشورة في مستوعبات سكوبس و كلاريفيت لأعضاء هيئة التدريس حسب العام الدراسي
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 12 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 2 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 38 |
4 | التمريض | 5 |
5 | الصيدلة | 4 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 13 |
7 | تقنيات الاجهزة الطبية | 11 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 8 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 21 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 77 |
4 | التمريض | 4 |
5 | الصيدلة | 11 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 16 |
7 | القانون | 1 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 22 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 36 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 29 |
4 | اللغة الإنكليزية | 2 |
5 | الصيدلة | 11 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 16 |
7 | االقانون | 3 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 10 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 11 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 12 |
4 | الهندسة المدنية | 12 |
Abstract Nowadays, technology is developed rapidly in communication technology. Several new technologies have been introduced due to the evolution of wireless communication and this provided the way to communicate among vehicles, using a Vehicular Ad-Hoc Network (VANETs). Routing in VANETs becomes most challenging because of the huge mobility and dynamical topology changes, which lead to reduced efficiency in the network. The core idea of this network is to increase the efficiency during the process of the communication. The most suited routing protocol for VANETs is Geographic routing, for the reason that it provides higher scalability and low overheads. The major challenges in VANETs are the selection of best neighbor in dynamically changing VANET topology. Furthermore, to provide better QoS needful actions are essential. In this paper, we introduced a new MAC/NET with Updated Genetic Algorithm—A Cross Layer Approach, (MNUG-CLA) based on a MAC layer and network layer to overcome the drawbacks of the network. In the network layer, a new neighbor discovery protocol is developed to select the best next hop for the dynamically varying network. In the MAC layer, in order to improve the quality, multi-channel MAC model is introduced for instantaneous transmission from various service channels. For overall optimal path selection, we used an updated GA algorithm. The performance was demonstrated through the use of an extensive simulation environment, NS-2. The simulation results prove that this protocol provides better results, in terms of energy efficiency, energy consumption and successive packet transmission, when compared with the earlier approaches.
- 2021

Mohammed Khalaf
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات



Abstract: In this project, the possibility of drug delivery application of three anti-Multiple sclerosis (MS) agents (containing diroximel fumarate (DXF), dimethyl fumarate (DMF), and mono methyl fumarate (MMF)) by using some heteroatom decorated graphitic carbonitride (g-C3N4) (as nano-sized carriers) have been systematically investigated. The results of the study have indicated that As-g-C3N4 QD is not a suitable candidate for drug delivery (at least in the cases of DMF, and DXF drugs); while, it would be an accurate semiconductor sensor for selective detection of each mentioned agents. Also, the use of the P-doped as well as pristine g-C3N4 QD could lead to weak electronic signals with relatively same values (in electronvolts). It means that P-g-C3N4, and g-C3N4 QDs are not good sensors for detection of each of the three considered drugs. However, those two sorbents would be suitable carriers for delivering of all three mentioned pharmaceuticals.
- 2023

SHIHAB HAMAD KHALEEFAH
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات

SHIHAB HAMAD KHALEEFAH
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract— Different software Quality Assurance (SQA) audit techniques are applied in the literature to determine whether the required standards and procedures within the Software Requirements Specification (SRS) phase are adhered to. The inspection of the Software Requirements Specification (iSRS) system is an analytical assurance tool which is proposed to strengthen the ability to scrutinize how to optimally create high-quality SRSs. The iSRS utilizes a Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) model in carrying out the SRS quality analysis based on the experience of the previously analyzed cases. This paper presents the contribution of integrating fuzzy Logic technique in the CBR steps to form a Fuzzy Case-Based Reasoning (FCBR) model for improving the reasoning and accuracy of the iSRS system. Additionally, for efficient cases retrieval in the CBR, relevant cases selection and nearest cases selection heuristic search algorithms are used in the system. Basically, the input to the relevant cases algorithm is the available cases in the system case base and the output is the relevant cases. The input to the nearest cases algorithm is the relevant cases and the output is the nearest cases. The fuzzy Logic technique works on the selected nearest cases and it utilizes similarity measurement methods to classify the cases into no-match, partial-match and complete-match cases. The features matching results assist the revised step of the CBR to generate a new solution. The implementation of the new FCBR model shows that converting numerical representation to qualitative terms simplifies the matching process and improves the decision-making of the system.
- 2019

SHIHAB HAMAD KHALEEFAH
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات



Abstract Autonomous agents and multi-agent systems significantly facilitate solutions to many complex and distributed problem-solving environments due to the agents’ various capabilities. These environments comprise uncertain, high dynamism or irregular workload that might prone the agents to make decisions that lead to undesirable outcomes. This paper proposes a Fuzzy Logic-based Adjustable Autonomy (FLAA) as a general framework for managing the autonomy of multi-agent systems that operate in complex environments. The framework includes a fuzzy logic technique to quantitatively measure and distribute the autonomy among operators (autonomous agents and humans) based on adjustable autonomy attributes. The FLAA framework dynamically changes the autonomy of the operators to directions that meets their ability to perform and produce desirable outcomes. The technical application of the framework is demonstrated by an example scenario. The scenario illustrates the competence performance of the collaborative operators. The advantages of using the framework are to capture relationships between discrete autonomy attributes, quantify adjustable autonomy and manage adjustable autonomous multi-agent systems
- 2018

Abstract;his research aims to build a general framework for choosing the most appropriate set of criteria for recruiting student as a research assistant in a university research project. University researchers could benefit from such a framework because it could optimize the costs of research while also enhancing students research skills. In the same time, it is also essential that the quality of research ought to measure up to the grants provided by the university. Nevertheless, it is a challenging problem for many research supervisors in the selection of qualified research assistants. In this paper, we attempted to resolve this problem by building a general framework for selecting the appropriate criteria in the evaluation of student performance. We explored earlier studies on the proposed evaluation criteria of the research assistant and identified 47 most impactful criteria criteria. We obtained experts in engineering and information technology fields from two universities to answer questionnaires to identify their commonly used criteria for grant research assistant (GRA). Then, all the identified criteria were evaluated using the fuzzy delphi method (FDM) for finding the best fitting criteria which resulted in 16 most impactful criteria.
- 2021

Abstract: Texture extraction of images is a core step in image pattern recognition applications. Different operators are applied for image texture extraction in order to obtain a unique identification of an image texture based on physical characteristics of the images. These operators are categorized into local and global texture analysis descriptors. This categorization is based on the properties of the operators and their features extraction methodology. However, each operator of a type has its strength and weakness in handling the deformations of the images including rotation, shear, region of interest, noise and variance of intensity. Subsequently, there is no operator that can perfectly handle all the deformation problems. To this end, this paper proposes a general framework of a Collaborative Multi-Agent Feature Extraction (CMAFE). The CMAFE framework deploys a multi-agent system to perform dynamic collaborations between the feature extraction operators. The operators are formed in a multi-agent system in which each agent implements an operator. This collaboration between the agents is based on a divide and conquer strategy. This strategy enables the operators to cope with the various challenges of deformations that are affecting the accuracy of the identification. The framework is meant to improve the image identification accuracy and reduce the universal search space of local and global operators which in return reduce the computational cost and time.
- 2018

Ahmed A Alsabhany
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


mustafa maad hamdi
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract in the single-source shortest path (SSSP) problem, the shortest paths from a source vertex v to all other vertices in a graph should be executed in the best way. A common algorithm to solve the (SSSP) is the A* and Ant colony optimization (ACO). However, the traditional A* is fast but not accurate because it doesn’t calculate all node’s distance of the graph. Moreover, it is slow in path computation. In this paper, we propose a new technique that consists of a hybridizing of A* algorithm and ant colony optimization (ACO). This solution depends on applying the optimization on the best path. For justification, the proposed algorithm has been applied to the parking system as a case study to validate the proposed algorithm performance. First, A*algorithm generates the shortest path in fast time processing. ACO will optimize this path and output the best path. The result showed that the proposed solution provides an average decreasing time performance is 13.5%
- 2019

Shumoos Taha Hammadi
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات



SHIHAB HAMAD KHALEEFAH
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract:The field of mobile communication has experienced great changes and growth since the advancement of computing devices and wireless technology. The need for mobile networks with minimal infrastructure that can be easily used, has been aroused by the mobility advancement of people around the world. Such kind of networks is known as Mobile Ad-hoc Networks (MANETs). The Ad Hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) is a popular routing protocol in the MANETs. Nevertheless, one issue of the AODV is the selection of routes based on minimum delay alone. Even though the delay is a significant parameter that has a direct effect on the performance of the network, other parameters such as energy consumption are necessary to establish efficiency routes. Therefore, this paper proposes employing a Multi-Agent System (MAS) for the establishment of efficient routes from the source to destination nodes in AODV, namely MAAODV protocol. The agents utilize the parameters of energy consumption, number of hops and delay to optimize the selection of the routes. The paper presents a simulation scenario to show the applicability of the proposed MAAODV routing protocol.
- 2018

SHIHAB HAMAD KHALEEFAH
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


ABSTRACT Advances in computer science have provided unique opportunities to apply Interactive Multimedia (IMM) courseware to a wide variety of medical and health care functions. Courseware can be called an easy to learn, teachable and course materials which is an important in Information Communication Technology world today. It helps the learners/students to improve their knowledge, skills and creativity. One area which holds the high ability for using computer systems is medical and health science education. This paper describes the design of an IMM courseware for learning about Human Heart. It proposes a Human Heart Anatomical and Functional Illustration (HHAFI) courseware for students, health officials and everyone interested in having a healthy heart. The HHAFI courseware is implemented by Toolbook Instructor and presented on Windows platform. The courseware includes an introduction that describes the heart and recall such as mechanisms of the heart, heart diseases, healthy tips and living a healthy lifestyle. The HHAFI courseware is tested with the student to identify the improvement in their knowledge and measure the level of interest in the topic. The HHAFI courseware provides learning and interactive training functions for interested individuals.
- 2019

Hazim Hakkush Al Dilaimy
- ابحاث قسم اللغة الانكليزية, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract A smart meter is an electronic device that accurately tracks your energy consumption and transmits that data to your energy provider so that you can be billed. The smart meters allow the central system and the meter to communicate in both directions. This two-way communication feature distinguishes the advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) in this case from automatic meter reading (AMR). This paper employs a hybrid system based on the Zigbee protocol, the Zigbee used to send messages between the smart meter and the utility company. To successfully complete tasks in this scenario, a cooperative communication system utilizing TDMA is used. The outcomes of Zigbee performance are measured using well-known metrics, also known as performance metrics. Many performance indicators have been chosen for performance evaluation: throughput, average end-to-end delivery ratio, and (PDR). The following conclusions were reached: End-to-end latency was 5.01 milliseconds, throughput was 42.63 kbps, and PDR was 97.19 percent. The network simulator successfully reads and wirelessly transmits voltage or power consumption using the Zigbee protocol and a cooperative communication system.
- 2021

dhafar hamed abd
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات

Mohammad H.Ellewe
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract:One of the most commonly used symmetric encryption methods is the Data Encryption Standard (DES), but it has a number of flaws. For instance, the encryption method only employs two functions (XOR), acts on one bit, and only allows for a finite number of combinations of data. To solve these issues, a new modified DES algorithm is presented in this study. The typical encryption DES algorithm of 16 rounds has been extended in the key space and the plaintext (using multiple keys) by presenting a new operation (Xo) replace the present XOR operation to increase complexity. In contrast to DES, which only employs one key, the research approach uses three keys other than the standard DES one. The input key for encryption and decryption processes is the first key. while other three keys are used to determine the table numbers (2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12), which have values ranging from 0 to 4096. When compared to the famous DES and other modified algorithms, the complexity analysis of the suggested method reveals it is the most difficult. As a result, the attacker must make atleast (4.7594738544661044544894020894748E+173) attempts to break the key and get the clear message. This indicates that the well-known DES security level will be raised by the suggested DES algorithm, depending on the new Xo function.
- 2023

Zainab Malik Ismael
- ابحاث قسم الهندسة المدنية, البحوث والدراسات


Mohammed Ahmed Talab
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات