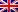
احصائيات البحوث المنشورة في مستوعبات سكوبس و كلاريفيت لأعضاء هيئة التدريس حسب العام الدراسي
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 12 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 2 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 38 |
4 | التمريض | 5 |
5 | الصيدلة | 4 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 13 |
7 | تقنيات الاجهزة الطبية | 11 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 8 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 21 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 77 |
4 | التمريض | 4 |
5 | الصيدلة | 11 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 16 |
7 | القانون | 1 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 22 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 36 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 29 |
4 | اللغة الإنكليزية | 2 |
5 | الصيدلة | 11 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 16 |
7 | االقانون | 3 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 10 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 11 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 12 |
4 | الهندسة المدنية | 12 |
Abstract A critical analysis of the approaches to the development of a model for determining the concentration of hazardous chemicals (HC) in the atmosphere, which are the basis of computeraided environmental monitoring systems (CEMS) has been carried out. It has been established that the lack of effective functioning of the existing CEMS is determined by the imperfection of the models used to determine the concentration of atmospheric chemical concentration in the atmosphere. In addition, the organic disadvantage of such systems is their departmental affiliation and, as a result, the limited number of potential users. To improve the efficiency of the discussed class of systems, a concept of integrated use has been proposed, within the CEMS framework, elements of information and analytical systems for environmental monitoring, satellite image processing tools, geoinformation technologies, and also mathematical software for calculating the concentration of various types of atmospheric HCs. Building a CEMS based on this concept will provide an opportunity to significantly improve the efficiency of their functioning in the aspects of reducing the time for making decisions, as well as reducing the risk of making wrong decisions. The mathematical support of the CEMS is based on the “Gaussian” statistical model of HC emission, and is intended, along with geographic information technologies, to synthesize a geomodel of groundlevel atmosphere pollution by HCs. As an illustrative example, the situation of the release of chemical waste in the area of Bila Tserkva (Kyiv region, Ukraine) is considered. Theoretical results form the methodological basis for the implementation of the applied information technology for the creation, deployment and operation of a decision support system for eliminating the consequences of an emergency situation caused by the proliferation of chemical water in the atmosphere
- 2018

Abstract A new method was established to estimate the ultimate load, which is utilized in the assessment of pile test. In the present study twenty five reports of failure test piles (28.5 x 28.5 cm in dimensions, 12 m in depth and the working load was 40 ton) of Um-Alqura Mosque project were studied in according to their loading and settlement. The (mean ± SD) of the pile settlement for each load of all piles studied were determined, and the results obtained were utilized to generate the equation that correlates between the load and settlement using (4th degree polynomial fit graph). The equation obtained was applied to estimate the ultimate load for the maximum settlement (10% of the pile diameter). The estimated ultimate load (130 ton) in the present study was compared with the ultimate load (132 ton), which was determined previously using (Fellenius and Decourt presentation, 2001). The deviation between the ultimate load of the previous and the present method was (1.5%), but the present method depends on two working load, so it saves time and efforts and suitable to implement in the assessment of the test pile.
- 2018

Abstract— The large network architecture of today consists of thousands of computers connected together through many interconnecting router and switches. As many of them communicate concurrently, congestion over the channels may increase. In order to maintain the fairness among the transmission control protocol (TCP) based packets being sent, during congestion each flow of communication must be treated fairly. The most popular scheduling scheme implemented today is the droptail, which it cannot guarantee fairness and as the queues get full; the latency increases. Therefore, packet drops cause reduction in throughput of those flows. Research is ongoing to find an Active Queue Management (AQM) scheme that can solve this fairness issue, though fairness is not the only important feature that is looked on. Latency is another feature, that is important as well as the packet loss ratio. In this paper, the performance of network metrics between the drop-tail and the behavior of different Active queue management schemes (PFIFO, RED, ARED, CoDel) in large networks is evaluated using the open source discrete network simulator (NS-3).
- 2018

Abstract Mobile Ad-hoc Networks (MANETs) are self-sufficient networks that can work without the need for centralized controls, pre-configuration to the routes or advance infrastructures. The nodes of a MANET are autonomously controlled, which allow them to act freely in a random manner within the MANET. The nodes can leave their MANET and join other MANETs at any time. These characteristics, however, might negatively affect the performance of the routing protocols and the overall topology of the networks. Subsequently, MANETs comprise specially designed routing protocols that reactively and proactively perform the routing. This paper evaluates and compares the performance of two routing protocols which are Ad-Hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) and Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR) in MANET environment. The study includes implementing a simulation to examine the performance of the routing protocols based on the variables of the nodes’ number and network size. The evaluation results show that the AODV outperforms the OLSR in most of the simulated cases. The results further show that the number of nodes and network size has a great impact on the Throughput (TH), Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR), and End-to-End delay (E2E) of the network.
- 2018

Abstract The most important and indispensable substance for life on earth is water. Regrettably, the growths of civilization, population, and industrssialization have led to a steady deterioration in the quality of available water resources. Heavy metals are a particular problem because of their high toxicity. This work highlights up-to-date methods for the removal of heavy metals from water using the technique of adsorption. After a comprehensive review of the range of materials used as adsorbents to remove heavy metals, the paper focuses on one particular technique, involving carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Tests have confirmed that CNTs are highly efficient, but have also revealed some drawbacks. Further adjustments and refinements are therefore required to improve their ability to remove heavy metals. This study shows that using deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as a functionalization agent to replace ionic liquids (ILs) has a number of advantages, including lower costs, easier availability of materials and environmentally friendliness. In sum, it suggests that the most efficient adsorption process is to use functionalized CNTs with DESs as an adsorbent. The critical analysis and conclusions emerging from this study should be of benefit to engineers, environmental scientists and chemists interested in the use of carbon nanotubes for use in environmental remediation.
- 2019

Abstract The most important and indispensable substance for life on earth is water. Regrettably, the growths of civilization, population, and industrssialization have led to a steady deterioration in the quality of available water resources. Heavy metals are a particular problem because of their high toxicity. This work highlights up-to-date methods for the removal of heavy metals from water using the technique of adsorption. After a comprehensive review of the range of materials used as adsorbents to remove heavy metals, the paper focuses on one particular technique, involving carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Tests have confirmed that CNTs are highly efficient, but have also revealed some drawbacks. Further adjustments and refinements are therefore required to improve their ability to remove heavy metals. This study shows that using deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as a functionalization agent to replace ionic liquids (ILs) has a number of advantages, including lower costs, easier availability of materials and environmentally friendliness. In sum, it suggests that the most efficient adsorption process is to use functionalized CNTs with DESs as an adsorbent. The critical analysis and conclusions emerging from this study should be of benefit to engineers, environmental scientists and chemists interested in the use of carbon nanotubes for use in environmental remediation.
- 2018

Abstracr As people with diabetes mellitus suffer from peripheral and autonomic neuropathy, we thought it possible that deficits in cognitive function might also be found. Our objective was to compare the cognitive function o f elderly persons with non-insulindependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) with a matched sample of persons without N
- 2018

abstract Aim: Diabetes mellitus is a spread disease in the whole world and this study was conducted on Iraqi diabetic men to know the relation between type II diabetic and some prostate related markers including (prostate size, total prostate antigen, random blood sugar and zinc). Material and methods: This study included one hundred men their age ranges between (40-60 year), fifty males were suffering from type II diabetes mellitus, and other fifty men were non-diabetics. Some parameters such as (Prostate size, total prostate specific antigen (tPSA), random blood sugar (RBS) and Zinc (Zn +2) were studied. Results: The results have showed significant increase in prostate size 50.5000 ± 3.748 and random blood sugar 203.55 ± 13.629 mg/dl compared with non-diabetic group 39.650 ± 2.484 and 125.750 ± 5.396 mg/dl, respectively but there is non-significant difference in total prostate specific antigen 1.543 ± 0.087 ng/ml and zinc 9.725 ± 0.344 µmol/l in diabetic group compared with non-diabetic group 1.612 ± 0.152 ng/ml and 11.025 ± 0.582 µmol/l respectively at P≤0.05.
- 2019

ABSTRACT This paper shedsthe light on the importance of audio-visual aids, for both the lecturers and learners at Al-Maarif University College. Those aids can serve as many functions in coaching English as a foreign language. Recently ithad a critical role in developing many institutions world wide. Every English education and learner must understand the various natures of audiovisual aids because he/ she can use those aids efficaciously in teaching English inside the classes.
- 2018

Mohammed Fawaz Sabah
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
ا.د. يعقوب ناظم احمد
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
ا.د. يعقوب ناظم احمد
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
Raed Obaid Saleh
- ابحاث قسم تقنيات المختبرات الطبية, البحوث والدراسات


ا.د. يعقوب ناظم احمد
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
ا.د. يعقوب ناظم احمد
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
ا.د. يعقوب ناظم احمد
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
ا.د. يعقوب ناظم احمد
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
Raed Obaid Saleh
- ابحاث قسم تقنيات المختبرات الطبية, البحوث والدراسات


ا.د. يعقوب ناظم احمد
- ابحاث قسم القانون, البحوث والدراسات
Abstract:Nowadays, 3D content is becoming an essential part of multimedia applications, when the 3D content is not protected, hackers may attack and steal it. This paper introduces a proposed scheme that provides high protection for 3D content by implementing multiple levels of security with preserving the original size using weight factor (w). First level of security is implemented by encrypting the texture map based on a 2D Logistic chaotic map. Second level is implemented by shuffling vertices (confusion) based on a 1D Tent chaotic map. Third level is implemented by modifying the vertices values (diffusion) based on a 3D Lorenz chaotic map. Results illustrate that the proposed scheme is completely deform the entire 3D content according to Hausdorff Distance (HD) approximately around 100 after the encryption process. It provides a high security against brute force attack because it has large key space equal to 10165 and secret key sensitivity using NPCR near 99:6% and UACI near 33:4%. The histogram and HD indicate the decrypted 3D content is identical to the origin where HD values approximate zero.
- 2023

Raed Obaid Saleh
- ابحاث قسم تقنيات المختبرات الطبية, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract Many researchers have been studying biological and managerial challenges of oil palm trees plantation and production. Oil Palm Pests and Diseases (OPPD), such as Oryctes rhinoceros beetles and Ganoderma are most prominent among the natural factors that deter the growth of oil palm trees and yields. Some of these OPPD have the properties of fast expansion and dynamic distribution making the monitoring of the OPPD a complex problem. Consequently, this paper proposes a risk assessment framework for Oil Palm Pests and Diseases Global Situation Awareness (OPPD-GSA). The OPPD-GSA framework operates by a teamwork of humans and software agents in a Collaborative Multi-agent System (CMAS). The overall system is implemented and experimentally tested in monitoring and controlling a sample OPPD observation data of Oryctes rhinoceros beetles and Ganoderma within five areas in Malaysia. The test results confirm that the OPPD-GSA application is able to process the OPPD monitoring tasks in real-time and handle Geo-located visualization data
- 2018

SHIHAB HAMAD KHALEEFAH
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات



Abstract In this study, the alkali-treated and untreated hybrid fibers incorporated with bio phenolic matrix to enhance the chemical interactions, mechanical and thermal properties have been investigated. The oil palm fiber (OPF) and pineapple fiber (PALF) were utilized as reinforcements into bio phenolic resin. The improvements in chemical interactions were monitored by the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer. The modifications of the surface for hybrid natural fibers (OPF/PALF) were enhanced in comparison to pure fiber composites. The composites’ dynamic mechanical behavior such as storage modulus, loss modulus, and damping properties were also investigated by dynamic mechanical analysis. Thermogravimetric analysis analyzed the performance of untreated (OPF and PALF) and treated (OPF/OPF) composites at elevated temperature and observed adequate interfacial bonding as a result of the improvements in thermal stability. The results presented that alkali) NaOH(incorporation in hybrid composites (OPF/PALF) results in increased the tensile strength and modulus among all composites. Furthermore, the tensile strength and modulus improved to the maximum value for treated 50% PALF composite compared to other composites. The hybridisation of treated alkali (5% NaOH/50% PALF) fiber shows best performance on tensile strength and modulus with 33.3 and 7535.2 MPa, respectively compared to other composites. The alkali-treated hybrid composites (NaOH/1OPF.1PALF) exhibited the greatest flexural strength (99.8 MPa) and modulus (8813.1 MPa). The enhancement of the interfacial adhesion between pure and hybrid fiber composites and bio phenolic matrix through the mercerisation of OPF and PALF fibers reinforced composite .
- 2021

Abstract Now days MIMO–OFDM is highly preferred in mobile communication, includes the 5th generation (long term evaluation). The objectives of current research include proposing and designing a high quality 5G cellular network using minimum resources and handover mechanism. The handover mechanism is implemented for the minimization of the time in the performance of the cellular network. The performance of the proposed simulation model for the 5G cellular network is extracted based resource allocation and handover mechanism. This implementation is reducing the handover preparation time and execution time. For the three selected schemes of transmission as − 5 dB, 0 dB, and 5 dB the experiment acts as an active, passive, and clustered. For the 0 dB the transmission acts as an active transmission, for the − 5 dB it acts as a passive, and for the 5db it acts as a clustered mode for the transmission. The present study clearly demonstrated that the 5G network can be communicated within minimum resources, time, space, and usability of the white spectrum with maximum speed. Due to the increasing complexity of network topology in 5G Heterogeneous with the integration of many different base station types, in the 5G architecture mobility management has many challenges. The intense deployment
- 2021