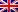
احصائيات البحوث المنشورة في مستوعبات سكوبس و كلاريفيت لأعضاء هيئة التدريس حسب العام الدراسي
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 12 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 2 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 38 |
4 | التمريض | 5 |
5 | الصيدلة | 4 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 13 |
7 | تقنيات الاجهزة الطبية | 11 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 8 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 21 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 77 |
4 | التمريض | 4 |
5 | الصيدلة | 11 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 16 |
7 | القانون | 1 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 22 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 36 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 29 |
4 | اللغة الإنكليزية | 2 |
5 | الصيدلة | 11 |
6 | الهندسة المدنية | 16 |
7 | االقانون | 3 |
ت | القسم | عدد البحوث |
1 | علوم الحاسوب | 10 |
2 | هندسة تقنيات الحاسوب | 11 |
3 | تقنيات المختبرات الطبية | 12 |
4 | الهندسة المدنية | 12 |
Abstract Face recognition from an image/video has been a fast-growing area in research community, and a sizeable number of face recognition techniques based on texture analysis have been developed in the past few years. Further, these techniques work well on gray-scale and colored images, but very few techniques deal with binary and low-resolution images. As the binary image is becoming the preferred format for low face resolution analysis, there is a need for further studies to provide a complete solution for the image-based face recognition system with a higher accuracy rate. To overcome the limitation of the existing methods in extracting distinctive features in low-resolution images due to the contrast between the face and background, we propose a statistical feature analysis technique to fill the gaps. To achieve this, the proposed technique integrates the binary-level occurrence matrix (BLCM) and the fuzzy local binary pattern (FLBP) named FBLCM to extract global and local features of the face from binary and low-resolution images. The purpose of FBLCM is to distinctively improve performance of edge sharpness between black and white pixels in the binary image and to extract significant data relating to the features of the face pattern. Experimental results on Yale and FEI datasets validate the superiority of the proposed technique over the other top-performing feature analysis methods. The developed technique has achieved the accuracy of 94.54% when a random forest classifier is used, hence outperforming other techniques such as the gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), bag of word (BOW), and fuzzy local binary pattern (FLBP), respectively.
- 2019

Abstract. Many types of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) are used to provide audio or multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, multimedia communications became very easy by using applications that provide Internet Protocol VoIP like Skype, Viber, WhatsApp, etc. And network simulation has frequently been used to determine the performance feasibility of any network protocols and the model reliability before practical implementation. Several kinds of studies were carried out on voice efficiency over different types of networks environment, among these experiments and researches, finding a better signaling protocol for communication by evaluating and analyzing the performance of the protocols, such as the most commonly used Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and (H.323) signaling protocols. This paper provides a comparative study of the performance of the two aforementioned protocols that are most widely used over the IEEE 802.11a wireless network by using the QualNet simulator. The study was performed by analyzing the data packets for both initiator and receiver for both protocols, to evaluate the performance based on five metrics: Session total Bytes, Establishment time, Sent, total Bytes received of Real-time transport protocol(RTP), Average End to End Delay and Overall Throughput. The outcomes demonstrated SIP protocol ascendingly rise and superior over H.323 protocol as a permanently started from the Zero-point around 5.4 (Mbps) of the time until the end of the experiment close to 6.2 with a 0.05-second delay while the rival was always below these values of throughput. Hence its superior provides preferability in multimedia sessions. studying and evaluate the performance of two IPs with a high capability simulator QualNet, SIP outright outperforms H.323 provide preferability recommendations in voice calls.
- 2021

Abstract
Abstract :Compared to other existing carbon nanomaterials (CNMs), carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are recognized for their significant properties. Despite their strong adsorption affinity, the difficulty of their dispersion and separation leads to limit their application in practical water treatment. Moreover, wastewater contamination by noxious organics, such as bisphenol A (BPA) and methylene blue (MB) dye compounds has become a world-wide environmental concern because they may be harmful to humans’ health and the ecosystem. Therefore, this article aims to explore the potential of economically directly growing CNTs on porous supports, such as the powder activated carbon (AC) to develop a multiscale hybridized material and to investigate their expected potential as viable adsorbents for removing persistent organic contaminants.
- 2020

Mustafa Mohammed Aljumaily
- ابحاث قسم الهندسة المدنية, البحوث والدراسات



Ahmed Shamil Mustafa
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract: The density of traffic is increasing daily in the world. As a result, congestion, accidents, and pollution are also increasing. Vehicular ad hoc network VANET, a subclass of mobile ad hoc networks MANETs, is a promising approach for future intelligent transportation system its. These networks have no fixed infrastructure and instead rely on the vehicles themselves to provide network functionality. In this review paper, we present an overview of the concept of vehicular ad hoc networks, applications, characteristics. also, we will provide discuss some of the issues and challenges in VANET.
- 2019

Abstract: The density of traffic is increasing daily in the world. As a result, congestion, accidents, and pollution are also increasing. Vehicular ad hoc network VANET, a subclass of mobile ad hoc networks MANETs, is a promising approach for future intelligent transportation system its. These networks have no fixed infrastructure and instead rely on the vehicles themselves to provide network functionality. In this review paper, we present an overview of the concept of vehicular ad hoc networks, applications, characteristics. also, we will provide discuss some of the issues and challenges in VANET.
- 2019

abstractA review of high-speed pipelined phase accumulator (PA) is proposed in this paper. The detail explanation of ideas, methods and techniques used in previous researches to improve the PA throughput designs were surveyed. The Brent-Kung (BK) adder was modified in this paper to be applied in pipelined PA architecture. A comparison of different adder circuits, includes a modified BK, ripple carry adder (RCA), Kogge-Stone adder (KS) and other prefix adders were applied to architect the PA based on Pipeline technique. The presented pipelined PA design circuit with multiple frequency control word (FCW) and different adders were coded Verilog hardware description language (HDL) code, compiled and verified with field programmable gate array (FPGA) kit platform. The comparison result shows that the modified BK adder has fast performances. The shifted clocking technique is utilized in the proposed technique), while preserving the high speed.
- 2019

Abdulkareem Dawah Abbas
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that affects one-third of the world’s population. Although currently available TB drugs have many side effects, such as nausea, headache and gastrointestinal discomfort, no new anti-TB drugs have been produced in the past 30 years. Therefore, the discovery of a new anti-TB agent with minimal or no side effects is urgently needed. Many previous works have reported the effects of medicinal plants against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). However, none have focused on medicinal plants from the Middle Eastern and North African (MENA) region. This review highlights the effects of medicinal plants from the MENA region on TB. Medicinal plants from the MENA region have been successfully used as traditional medicine and first aid against TB related problems. A total of 184 plants species representing 73 families were studied. Amongst these species, 93 species contained more active compounds with strong anti-MTB activity (crude extracts and/or bioactive compounds with activities of 0-100 µg/ml). The extract of Inula helenium, Khaya senegalensis, Premna odorata and Rosmarinus officinalis presented the strongest anti-MTB activity. In addition, Boswellia papyrifera (Del) Hochst olibanum, Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh leaves (river red gum), Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds and genus Cymbopogon exhibited anti-TB activity. The most potent bioactive compounds included alantolactone, octyl acetate, 1,8-cineole, thymoquinone, piperitone, α- verbenol, citral b and α-pinene. These compounds affect the permeability of microbial plasma membranes, thus kill the mycobacterium spp. As a conclusion, plant species collected from the MENA region are potential sources of novel drugs against TB.
- 2019

Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that affects one-third of the world’s population. Although currently available TB drugs have many side effects, such as nausea, headache and gastrointestinal discomfort, no new anti-TB drugs have been produced in the past 30 years. Therefore, the discovery of a new anti-TB agent with minimal or no side effects is urgently needed. Many previous works have reported the effects of medicinal plants against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). However, none have focused on medicinal plants from the Middle Eastern and North African (MENA) region. This review highlights the effects of medicinal plants from the MENA region on TB. Medicinal plants from the MENA region have been successfully used as traditional medicine and first aid against TB related problems. A total of 184 plants species representing 73 families were studied. Amongst these species, 93 species contained more active compounds with strong anti-MTB activity (crude extracts and/or bioactive compounds with activities of 0-100 µg/ml). The extract of Inula helenium, Khaya senegalensis, Premna odorata and Rosmarinus officinalis presented the strongest anti-MTB activity. In addition, Boswellia papyrifera (Del) Hochst olibanum, Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh leaves (river red gum), Nigella sativa (black cumin) seeds and genus Cymbopogon exhibited anti-TB activity. The most potent bioactive compounds included alantolactone, octyl acetate, 1,8-cineole, thymoquinone, piperitone, α- verbenol, citral b and α-pinene. These compounds affect the permeability of microbial plasma membranes, thus kill the mycobacterium spp. As a conclusion, plant species collected from the MENA region are potential sources of novel drugs against TB.
- 2019

Mohamed Khalid AlOmar
- ابحاث قسم الهندسة المدنية, البحوث والدراسات



Ali Sami Dheyab
- ابحاث قسم تقنيات المختبرات الطبية, البحوث والدراسات



Abstract: In recent ten years, wireless sensor network technology has a rapid development. After a brief introduction of the wireless sensor network, some main research results of energy conservation and node deployment is provided. Then the applications of WSN in the medical health, environment and agriculture, intelligent home furnishing and building, military, space and marine exploration are outlined. In addition, we analyze the advantage of WSN in these areas. Finally, we summarize the main factors that affect the applications of wireless sensor network
- 2021

Abstract Aiming at the problem that it is difficult to achieve rapid and accurate detection of pesticide residues, the artificial neural network method is used to separate the mixed fluorescence spectra in the measurement of acetamiprid pesticide residues, and a fluorescence spectrum that can quickly detect the pesticide residues of acetamiprid on solid surfaces is designed. According to the back-propagation algorithm, the three-layer artificial neural network principle is used to detect the acetamiprid residue in the mixed system of acetamiprid and filter paper with severely overlapping fluorescence spectra. In the range of 340nm~400nm, using the fluorescence intensity values at 20 characteristic wavelengths as the characteristic network parameters, after network training and testing, the recovery rates of acetamiprid concentrations of 40mg/kg and 90mg/kg are 102% and 97%, respectively. The relative standard deviations of the determination results were 1.4% and 1.9%, respectively. The experimental results show that the BP neural network-assisted fluorescence spectroscopy method for the determination of acetamiprid pesticide residues on filter paper has the characteristics of fast network training, short detection period, and high measurement accuracy.
- 2021

mustafa maad hamdi
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات

mustafa maad hamdi
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Abstract:Ad hoc vehicle networks (VANET) are being established as a primary form of mobile ad hoc networks (MANET) and a critical infrastructure to provide vehicle passengers with a wide range of safety applications. VANETs are increasingly common nowadays because it is connecting to a wide range of invisible services. The security of VANETs is paramount as their future use must not jeopardize their users’ safety and privacy. The security of these VANETs is essential for the benefit of secure and effective security solutions and facilities, and uncertainty remains, and research in this field remains fast increasing. We discussed the challenges in VANET in this survey. Were vehicles and communication in VANET are efficient to ensure communication between vehicles to vehicles (V2V), vehicles to infrastructures (V2I). Clarified security concerns have been discussed, including confidentiality, authentication, integrity, availableness, and non-repudiation. We have also discussed the potential attacks on security services. According to analysis and performance evaluations, this paper shows that the ACPN is both feasible and appropriate for effective authentication in the VANET. Finally, the article found that in VANETs, encryption and authentication are critical.
- 2021

mustafa maad hamdi
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Ahmed Shamil Mustafa
- ابحاث قسم هندسة الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Saade Abdalkareem Jasim
- ابحاث قسم تقنيات المختبرات الطبية, البحوث والدراسات


ABSTRACT Pseudomonas aeruginosa This is study aimed to review previous studies that explain the causes of multiple resistance to these bacteria, and they are also considered Nosocomail bacteria. These bacteria most often infect immunocompromised people, and treatment is often difficult and complicated for those infected due to multiple resistance. This review also demonstrated the benefit of using plant extracts and aromatic oils as alternatives to antibiotics as an inhibitor against P. aeruginosa. During previous studies, it was shown that most of the isolates were distributed among burn infections, wounds, urinary and respiratory tract infections, sputum, and blood poisoning. In addition, this review focused on virulence genes and their major role in bacterial resistance to antibiotics, as well as identifying the main P. aeruginosa genes to be used in the speed of diagnosis. Among the most important of these virulence factors is biofilm formation, β-lactamase production, Pyocyanins, and other enzymes. This review also identified the differences between clinical and environmental isolates and the extent of the effect of random use of antibiotics and the modifications that occurred to bacteria that made them resistant to these antibiotics
- 2019

Dhafar Hamed Abd
- CS Dept Research, ابحاث قسم الحاسوب, البحوث والدراسات


Mohanad Hazim Hakkoosh
- ابحاث قسم اللغة الانكليزية, البحوث والدراسات

Marwah Firas Abdullah Al-Rawe
- ابحاث قسم اللغة الانكليزية, البحوث والدراسات